

Weak foundation, silty clayey sand layer (AC1) and liquefied layers (AC1 and fine sand AS22) below the slope were observed as the main reasons for this small impact of geotextile. However, the impact of geotextile is very limited in this case that only decrease 0.109m or about 20% from the total displacement without geotextile. The strengthening method using geotextile (500 kN/m tensile strength, 5004 kN/m axial stiffness, 30m length in 5 layers) decreased the total displacement from 0.543m to 0.434m. Further dynamic analysis was also completed using PLAXIS 2D with UBCSAND model to calculate the total displacement at slope crest without and with geotextile application. The value of safety factor at 1.93 was obtained then compared to the result for the same problem based on the Finite Element Method using PLAXIS 2D with HS Small model that resulted at 2.07 safety factor.
PLAXIS 2D FOR SLOPE STABILITY ANALYSIS SOFTWARE
Limit Equilibrium Method using D-Geo stability software based on the Bishop method was taken to define safety factor of slope under uniform load (without earthquake load).
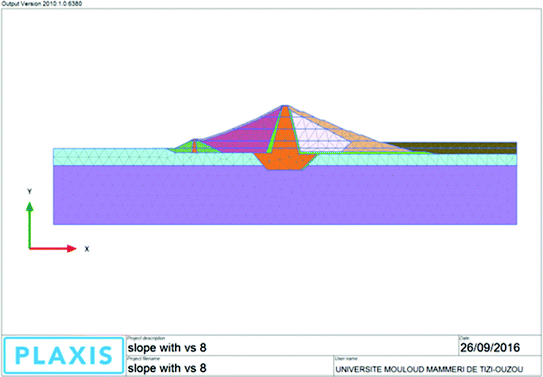
Furthermore, analyses based on the Limit Equilibrium method and Finite Element Method were selected to analyse the slope stability. The average values of N-SPT were calculated for further parameter correlations based on these values. Six layers that mostly consist of sandy soils were determined based on the SPT data in 16 locations. Two loads acted on the slope such as the uniform load on top of the raised area and dynamic load from the earthquake were defined. A cross-section of slope with 0.435m height and 29 degrees slope angle were chosen for the geometry of analysis. This project discussed the analysis of geotextile-reinforced slope by comparing the total displacement at the crest of slope between the compaction method as current design and the using of geotextile with further investigation by optimising the use of geotextile application. Therefore, this research examines the impact of geotextile application on slope stability in newly-elevated area in Yuriage, Natori City, Japan. The use of geotextile for slope strengthening was proven based on the investigation and report by Kuwano, Miyata, and Koseki (2014). Mustaqim, Mustaqim (TU Delft Civil Engineering and Geosciences) The analysis included determination of FoS as well as a sensitivity analysis looking into the combined effects of contributing parameters.Stability Analysis of Geotextile-reinforced Slope Based on Japan Earthquake in 2011: Yuriage, Natori City Case In this research study, limit-equilibrium and finite-element methods are used by the Oasys slope and Plaxis 2D software programs, respectively, empirically and numerically to model and analyse geometrically non-homogeneous stratified slopes with the aim of understanding the effects of non-homogeneity of geometry and materials on stability under various inclination angles of slope face. The current practice in analysing slopes of complicated nature, geometrically and materially, is mostly to apply simplifications sacrificing accuracy leading to use of large factors of safety (FoS), which could undermine analytical and economic feasibility of projects.
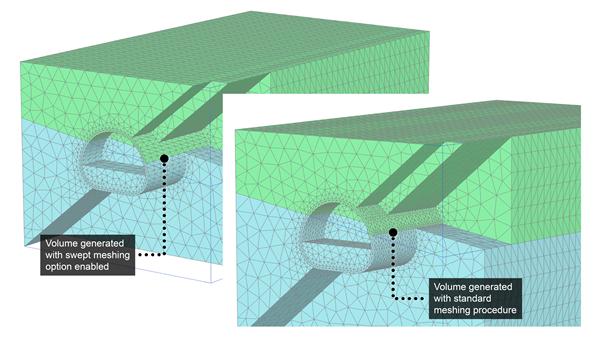
As most natural slopes are of non-homogeneous layered nature, understanding the stability behaviour of such slopes will be of utmost importance. Urbanisation means that many natural slopes in and around cities are often subjected to cuts resulting in dramatic changes in the geometry of slope faces mostly by increasing slope angle, which could lead to failures with catastrophic consequences.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
